
Introduction to satellite Communications. Lecture (11). What is a satellite ?. S atellite is an object launched to orbit earth or another celestial body. How it works. Features of Satellites:. Providing global coverage. Carrying large amount of traffic

greenkevin + Follow
Download PresentationAn Image/Link below is provided (as is) to download presentation Download Policy: Content on the Website is provided to you AS IS for your information and personal use and may not be sold / licensed / shared on other websites without getting consent from its author. Content is provided to you AS IS for your information and personal use only. Download presentation by click this link. While downloading, if for some reason you are not able to download a presentation, the publisher may have deleted the file from their server. During download, if you can't get a presentation, the file might be deleted by the publisher.

Satellite Communications CSC 490: Wireless Networking Author: Michael Charles Overview Basics of Satellites Types of Satellites Capacity Allocation Basics: How do Satellites Work
1.9k views • 27 slides

Lecture 2.9 Module 2. AVIATION TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEMS Topic 2.9. AVIATION SATELLITE COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS. Satellite Communications. Satellite-Related Terms. Earth Stations – antenna systems on or near earth Uplink – transmission from an earth station to a satellite
935 views • 34 slides

Satellite Communications. COE 341 Term Paper. Groupe Members. Aref Mohammad Al-Amri. Ahmad Abdulrahman Al-Gahtani. Ahmad Abdullah Al-Aloula. Topics of Presentation. Intro. Lunching. Applications. Satellites. How it works. Frequency Bands. What are Communication Satellites?.
573 views • 12 slides

Class Contents. Satellite Parameters and ConfigurationsSatellite OrbitsFrequency BandsTransmission ImpairmentsSatellite Network ConfigurationsCapacity Allocation Frequency DivisionFDM (Frequency Division Multiplexing)FDMA (Frequency Division Multiple Access)Capacity Allocation Time Div
1.02k views • 39 slides

Satellite Communications. Chapter 9. Satellite-Related Terms. Earth Stations – antenna systems on or near earth Uplink – transmission from an earth station to a satellite Downlink – transmission from a satellite to an earth station
739 views • 24 slides

Satellite Communications. DirecTV and Satellite Radio. Overview. Direct Broadcast Satellite DirecTV Satellite Radio Background Common Technology Competitors XM SIRIUS WorldSpace. Direct Broadcast Satellite (DBS). Direct Broadcast Satellite Refers to either Television Service
674 views • 14 slides

Satellite Communications. CSC 490: Wireless Networking Author: Michael Charles. Overview. Basics of Satellites Types of Satellites Capacity Allocation. Basics: How do Satellites Work.
1.08k views • 27 slides

Satellite Communications. Prepared by Kenneth J. Buonforte Much Thanks to Tom Fronckowiak. Differences Between Satellite-Based and Terrestrial Wireless. Satellite-system has greater area of coverage Spacecraft power and allocated bandwidth are limited resources
699 views • 33 slides

Factors in satellite communication
498 views • 27 slides

SATELLITE COMMUNICATIONS. Engr. Cezar N. Velasco Jr. Satellite. A spacecraft placed in orbit around the earth which carries on board microwave receiving and transmitting equipment; repeater, capable of relaying signals from one point on earth to other points.
428 views • 17 slides

SATELLITE COMMUNICATIONS. BISHOY MOFIED OMAR SHAABAN VARTAN SHOUSHANIAN. 1. Outline. Introduction How satellite works History of satellites Satellite Frequency Bands Digital modulation schemes Satellite components Orbital altitudes GPS satellites Antenna Gain efficiency
1.12k views • 42 slides

Wireless and Mobile Networks. Ch7: Satellite Communications. Overview. Basics of Satellites Types of Satellites Capacity Allocation. Satellite Services & Applications. Voice/Video/Data Communications Rural Telephony News Gathering/Distribution Internet Trunking
735 views • 41 slides

Satellite Communications. Alison Griffiths – Room C203, Beacon Building a.l.griffiths@staffs.ac.uk. MCCS. What we will look at What are satellite phones How do they operate How do they integrate into the PSTN network Who operates this phone network. MCCS.
536 views • 27 slides

Satellite Communications. Learning Objectives:. At the end of this topic you should be able to: describe satellite communications, give examples of typical applications of satellite communications. explain the advantages and disadvantages of satellite communications,.
975 views • 57 slides

Satellite Communications-II. Dr. Nasir D. Gohar. Satellite Communications-II. WHY MULTIPLE ACCESS? Users/Earth Stations Share the Transmission Resource i.e. Radio Spectrum
735 views • 36 slides

Satellite Communications. Chris Webster NSF Users Workshop 2007 NCAR - EOL. Reasons / Motivation. Safety situational awareness Remote real-time instrument monitoring Remote real-time science Remote real-time instrument control Project coordination Troubleshooting. History.
322 views • 16 slides

Satellite Communications. Introduction and Historical Background. What is a Satellite?. Satellite: In astronomical terms , a satellite is a celestial body that orbits around a planet. Example: The moon is a satellite of Earth.
1.07k views • 17 slides

Get the best maritime satellite communications services at sea side.
301 views • 2 slides

SATELLITE COMMUNICATIONS. Dr. C. SARITHA Lecturer in Electronics SSBN Degree College ANANTAPUR. Contents…. Introduction Orbit Keplers laws Frequency Allocation Advantages of satellite/ Applications Disadvantages Conclusion. Introduction.
2.09k views • 57 slides

Satellite Communications. Chris Webster NSF Users Workshop 2007 NCAR - EOL. Reasons / Motivation. Safety situational awareness Remote real-time instrument monitoring Remote real-time science Remote real-time instrument control Project coordination Troubleshooting. History.
327 views • 16 slides
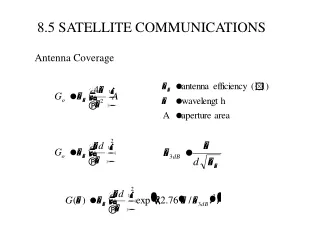
8.5 SATELLITE COMMUNICATIONS. Antenna Coverage. Figure 8-29. (a) Satellite repeater link. (b) Frequency-translation satellite communications relay. (c) Demod/remod satellite communications relay. Figure 8-30 Polar representation of a general antenna gain function. Example 8.4.
339 views • 28 slides

Presentation by Ron Herring W7HD. Satellite Communications. Communication factors. Communication factors part 2. Factors in Communication part 3. How distance affects loss. What the atmosphere does to satellite communication. Frequency bands.
510 views • 42 slides